

Cam and Camshaft: It is provided to operate the opening and closing of the Inlet and Exhaust valve and also operate the fuel injection pump in the Diesel engine.Cooling fins or Water jackets: It is used for cooling purposes.Crankshaft: It is the rotating member, which connects the crank.Connecting rod: It is used to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston to rotary motion of the crankshaft.It is also used as the sump of lubricating oil. Crankcase: It is the housing of crank and other engine parts.

It makes a circular motion inside the crankcase. It seals the gap between the cylinder liner and piston. Piston rings: Two or three piston rings are provided on the piston.Piston: It is the reciprocating member of the engine.Cylinder head: It is the top cover of the cylinder, towards TDC, which is called the cylinder head.Cylinder: It is the heart of the engine.This ratio is the difference between the minimum and maximum volume in the engine chamber A higher ratio will allow a larger fuel-air mixture to enter, causing higher pressure, leading to a hotter chamber, which increases thermal efficiency.įour-stroke engines consist of the following parts: One way thermodynamic efficiency can improve in engines is through a higher compression ratio. However, in general, gasoline engines convert 20% of the fuel (chemical energy) to mechanical energy in which only 15% will be used to move the wheels. The thermal efficiency of these gasoline engines will vary depending on the model and design of the vehicle. The remaining exhaust gas is pushed out by the piston as it moves back upwards.
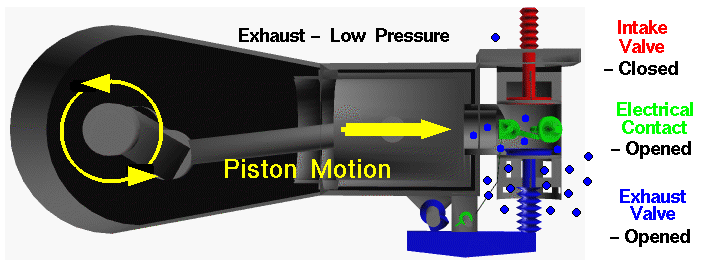

Power Stroke: As the fuel reaches the end of its combustion, the heat released from combusting hydrocarbons increases the pressure which causes the gas to push down on the piston and create the power output.At the end of this stroke, a spark plug provides the compressed fuel with the activation energy required to begin combustion. Compression stroke: The intake valve is closed, and the piston moves up the chamber to the top.Intake stroke: The piston moves downward to the bottom this increases the volume to allow a fuel-air mixture to enter the chamber.There is an animation of a four-stroke engine and a further explanation of the process below. The four-stroke engine is the most common type of internal combustion engine and is used in various automobiles that specifically use gasoline as fuel like cars, trucks, and some motorbikes.Ī four-stroke engine delivers one power stroke for every two cycles of the piston (or four-piston strokes).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
